SOM Product Comparison Guide
-
Product MCM-iMX95 UCM-iMX95 UCM-iMX8M-Plus CL-SOM-iMX8Plus MCM-iMX93 UCM-iMX93L UCM-iMX93 UCM-iMX91L MCM-iMX8M-Mini UCM-iMX8M-Mini SoC Family Form Factor Connection Type Size (mm) Introduced Longevity NXP i.MX95 SMD solder-down 180-pad soldered QFN 34 x 42 x 3 2025 until 2039 NXP i.MX95 UCM pin2pin 2x 100-pin mezzanine 28 x 40 x 5 2024 until 2039 NXP i.MX8M Plus UCM pin2pin 2x 100-pin mezzanine 28 x 38 x 5 2021 until 2036 NXP i.MX8M Plus SODIMM 204-pin edge 36 x 68 x 5 2021 until 2036 NXP i.MX93 SMD solder-down 140-pad soldered QFN 30 x 30 x 3 2024 until 2038 NXP i.MX93 UCM pin2pin 2x 100-pin mezzanine 28 x 30 x 4 2023 until 2038 NXP i.MX93 UCM pin2pin 2x 100-pin mezzanine 28 x 38 x 4 2023 until 2038 NXP i.MX91 UCM pin2pin 2x 100-pin mezzanine 28 x 30 x 4 2024 until 2039 NXP i.MX8M Mini SMD solder-down 140-pad soldered QFN 30 x 30 x 3 2020 until 2035 NXP i.MX8M Mini UCM pin2pin 2x 100-pin mezzanine 28 x 38 x 4 2019 until 2035 -
Product MCM-iMX95 UCM-iMX95 UCM-iMX8M-Plus CL-SOM-iMX8Plus MCM-iMX93 UCM-iMX93L UCM-iMX93 UCM-iMX91L MCM-iMX8M-Mini UCM-iMX8M-Mini CPU Cores RAM Storage Real-Time
Co-processorGPU AI/ML
NPU6x Cortex-A55, 2.0GHz 4GB – 16GB 16GB - 128GB Cortex-M7 ARM Mali GPU up to 2.0 TOPS 6x Cortex-A55, 2.0GHz 4GB – 16GB 16GB - 128GB Cortex-M7 ARM Mali GPU up to 2.0 TOPS 4x Cortex-A53, 1.8GHz 1GB – 8GB 16GB - 128GB Cortex-M7 GC7000UL GPU up to 2.3 TOPS 4x Cortex-A53, 1.8GHz 1GB – 8GB 16GB - 128GB Cortex-M7 GC7000UL GPU up to 2.3 TOPS 2x Cortex-A55, 1.7GHz 512MB – 2GB 8GB - 64GB Cortex-M33 - up to 0.5 TOPS 2x Cortex-A55, 1.7GHz 512MB – 2GB 8GB - 64GB Cortex-M33 - up to 0.5 TOPS 2x Cortex-A55, 1.7GHz 512MB – 2GB 8GB - 64GB Cortex-M33 - up to 0.5 TOPS 1x Cortex-A55, 1.4GHz 512MB – 2GB 8GB - 64GB - - - 4x Cortex-A53, 1.8GHz 1GB – 4GB 4GB - 64GB Cortex-M4 GC NanoUltra GPU - 4x Cortex-A53, 1.8GHz 1GB – 4GB 4GB - 64GB Cortex-M4 GC NanoUltra GPU - -
Product MCM-iMX95 UCM-iMX95 UCM-iMX8M-Plus CL-SOM-iMX8Plus MCM-iMX93 UCM-iMX93L UCM-iMX93 UCM-iMX91L MCM-iMX8M-Mini UCM-iMX8M-Mini Display
InterfacesMax
ResolutionVideo
DecodingCamera
InterfacesVideo
Encoding2x LVDS, MIPI-DSI 4096 x 2160 4Kp60 2x MIPI-CSI, 4 lanes 4Kp60 2x LVDS, MIPI-DSI 4096 x 2160 4Kp60 2x MIPI-CSI, 4 lanes 4Kp60 HDMI, LVDS, MIPI-DSI 1920 x 1080 1080p60 2x MIPI-CSI, 4 lanes 1080p60 HDMI, LVDS, MIPI-DSI 1920 x 1080 1080p60 2x MIPI-CSI, 4 lanes 1080p60 LVDS, MIPI-DSI, parallel RGB 1920 x 1080 - MIPI-CSI, 2 lanes - LVDS, MIPI-DSI 1920 x 1080 - MIPI-CSI, 2 lanes - LVDS, MIPI-DSI 1920 x 1080 - MIPI-CSI, 2 lanes - - - - - - MIPI-DSI 1920 x 1080 1080p60 MIPI-CSI, 4 lanes 1080p60 MIPI-DSI 1920 x 1080 1080p60 MIPI-CSI, 4 lanes 1080p60 -
Product MCM-iMX95 UCM-iMX95 UCM-iMX8M-Plus CL-SOM-iMX8Plus MCM-iMX93 UCM-iMX93L UCM-iMX93 UCM-iMX91L MCM-iMX8M-Mini UCM-iMX8M-Mini Ethernet WiFi BT USB 3.0 USB 2.0 PCIe UART CAN SDIO SPI I2C GPIO 2x RGMII - - 1 1 2 8 5 2 8 6 88 1x GbE + 1x RGMII + 10 GbE 802.11ax 5.3 1 1 2 8 5 2 8 7 94 1x GbE + 1x RGMII - - 2 - 1 4 2 2 2 5 75 2x GbE / RGMII 802.11ac 5.3 2 - 1 4 2 2 3 6 90 2x RGMII - - - 2 - 8 2 2 8 6 80 1x GbE + 1x RGMII - - - 2 - 7 2 2 7 6 65 1x GbE + 1x RGMII 802.11ac 5.3 - 2 - 7 2 2 7 6 79 1x GbE + 1x RGMII - - - 2 - 7 2 2 7 6 65 1x RGMII - - - 2 1 4 - 2 3 3 86 1x GbE / RGMII 802.11ac 4.2 - 2 1 4 - 1 3 3 85 -
Product MCM-iMX95 UCM-iMX95 UCM-iMX8M-Plus CL-SOM-iMX8Plus MCM-iMX93 UCM-iMX93L UCM-iMX93 UCM-iMX91L MCM-iMX8M-Mini UCM-iMX8M-Mini Linux Kernel Yocto Debian FreeRTOS 6.12 ✓ ✓ ✓ 6.12 ✓ ✓ ✓ 6.6 ✓ ✓ ✓ 6.6 ✓ ✓ ✓ 6.6 ✓ ✓ ✓ 6.6 ✓ ✓ ✓ 6.6 ✓ ✓ ✓ 6.6 ✓ ✓ ✓ 6.6 ✓ ✓ ✓ 6.6 ✓ ✓ ✓
System-on-Module Selection Guidelines
Form-Factor and Connection Type
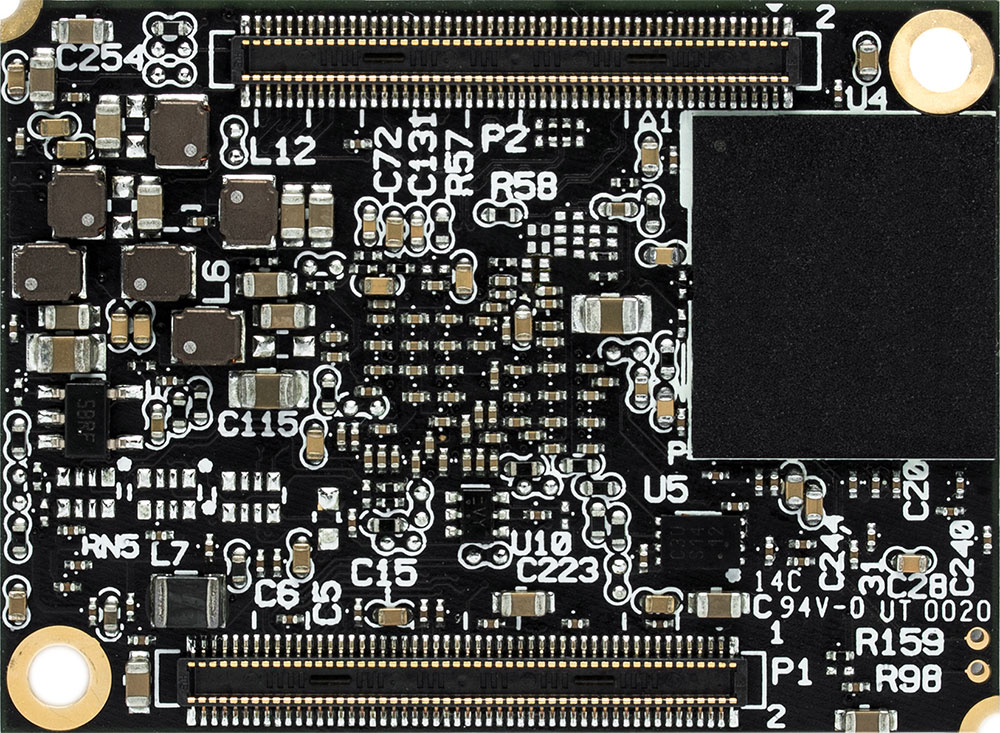
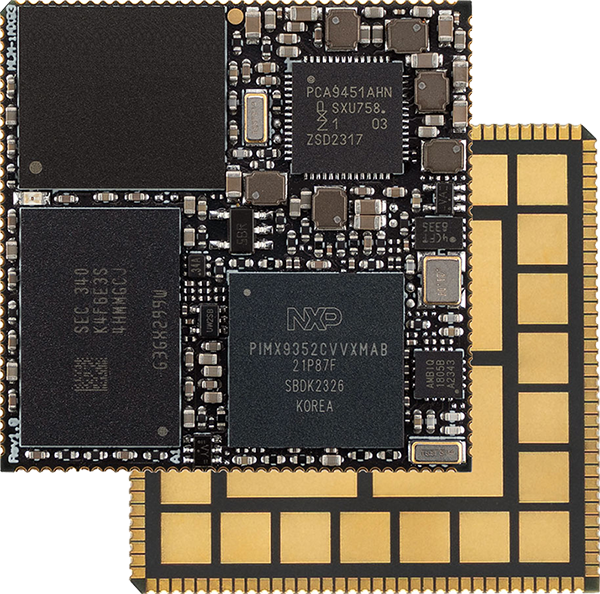
There are three main types of System on Module form-factors – edge connector SOMs, mezzanine connector SOMs and solder-down SOMs.
| Edge Connector | Mezzanine Connectors | SMD Solder-Down | |
|---|---|---|---|
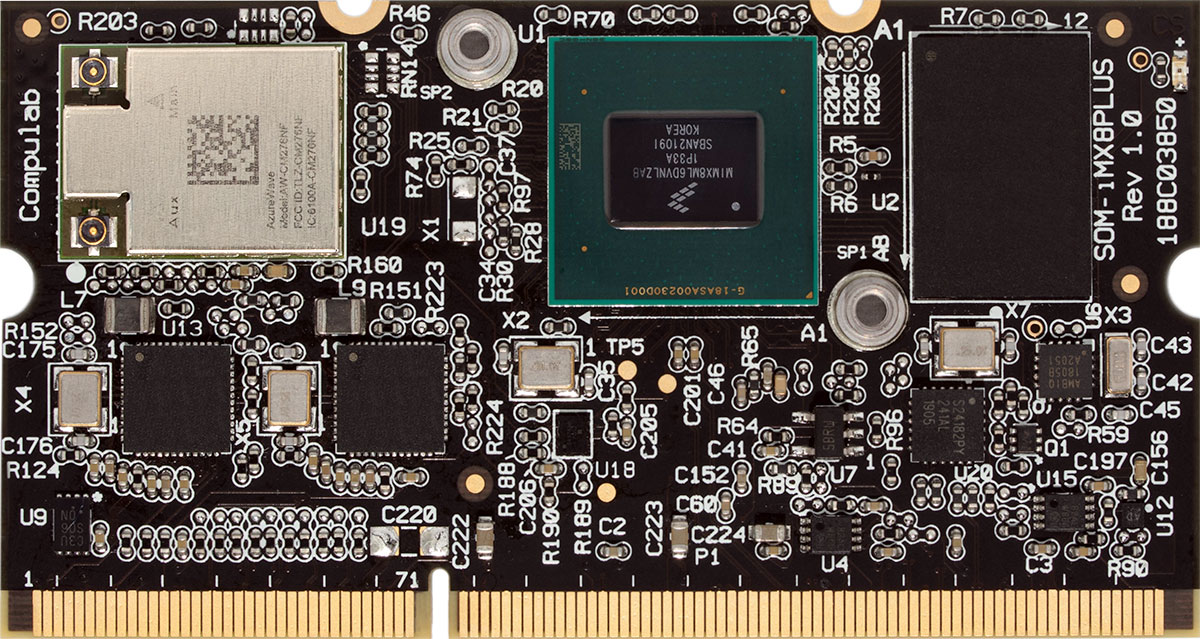 |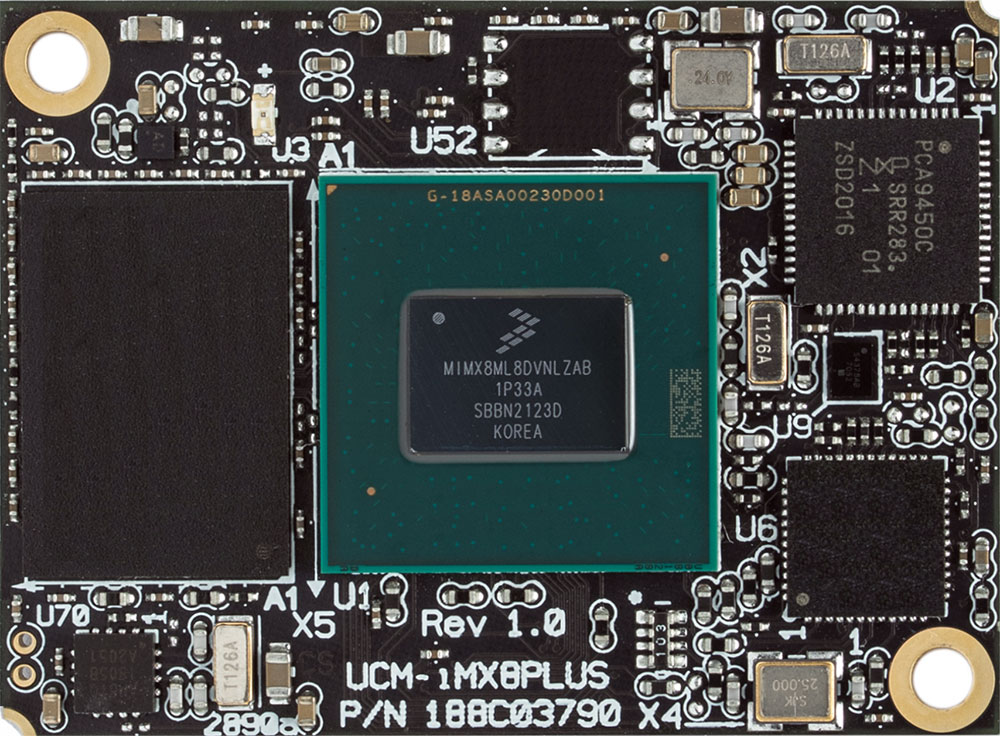  |  |  |
- Edge connector SOMs are very common. The main downside of these boards is inherently larger foot-print, due to the constraints of the edge connector length. Also, keep in mind that the body of the mating connector takes up board space – in addition to the size of the SOM itself.
- Mezzanine connector SOMs usually allow more efficient board space utilization with no apparent drawbacks.
- Solder-down SOMs offer several unique advantages such as enhanced mechanical robustness, reduced height profile and automated assembly. For additional information refer to Advantages of solder-down System-on-Modules.
Long-Term Availability
Long-term availability is absolutely crucial for most industrial projects. In some applications where design and certification cycles are very long, it can take 3 to 5 years for a product to begin mass production. In other cases, companies might need to re-use the same design in several different projects.
It is highly recommended to choose a SOM which has at least 10 years of guaranteed availability from the beginning of your project.
Software Packages
Board support packages for boot-loader and operating system are an integral part of any System on Module.
Verify that the SOM is provided with full BSP for the O/S you plan to use. It is also recommended to review the supporting documentation.
Connectivity
Not all System on Modules expose all SoC signals. Furthermore, most ARM SoCs use signal multiplexing, which imposes limitations on the set of functions you can use simultaneously.
Ensure that the required signals are in fact available in the SOM you choose and that there are no collisions between the functions.
Configurability
Some System on Module are offered with configurable options such as different RAM and storage capacities and optional peripherals. This approach allows customers to select the exact features needed for their application and optimize SOM cost.
Consider what configuration you would need for your project.
Power Consumption and Heat Dissipation
Verify that the selected SOM fits within the power budget of your system. SOM power consumption significantly depends on the specific use case and processing load. Reputable SOM vendors normally provide detailed power consumption data for different typical use cases.
Consider whether the SOM in your design will require a heat-dissipation solution. Check whether the SOM is provided with a heat-plate or heat-sink.